ISO 17992 pdf download
ISO 17992 pdf download Iron ores — Determination of arsenic content — Hydride generation atomic absorption spectrometric method
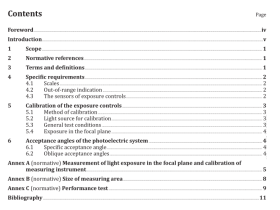
1 Scope
This International Standard specifies a hydride generation atomic absorption spectrometric method for the determination of the arsenic content of iron ore.
This International Standard is applicable to mass fractions of arsenic between 0,000 66 % and 0,020 15 % in natural iron ores, iron ore concentrates and agglomerates, including sinter products.
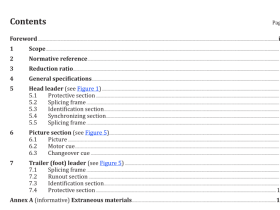
2 Normative references
The following documents, in whole or in part, are normatively referenced in this document and are indispensable for its application. For dated references, only the edition cited applies. For undated references, the latest edition of the referenced document (including any amendments) applies.
ISO 648, Laboratory glassware — Single-volume pipettes
ISO 1042, Laboratory glassware — One-mark volumetric flasks
ISO 3082, Iron ores — Sampling and sample preparation procedures
ISO 3696, Water for analytical laboratory use — Specification and test methods
ISO 7764, Iron ores — Preparation of predried test samples for chemical analysis
ISO Guide 35:2006, Reference materials — General and statistical principles for certification
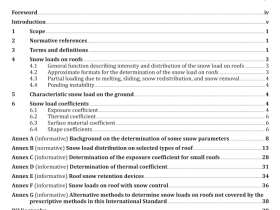
3 Principle
The test portion is decomposed by treatment with hydrochloric and nitric acid. The residue is treated with sodium peroxide and sodium carbonate. Potassium iodide reduces As(V) to As(III) and ascorbic acid masks the effect of iron in the solution. At optimum acidity of around 26 %, the solution and sodium borohydride react to generate gaseous arsenic hydride. An inert carrier gas is used to transport the arsenic hydride to a quartz tube atomizer. The equipment is set to measure the absorbances at 197,3 nm. The absorbances of the test and calibration solutions, including those of certified or other reference materials, are compared to determine the arsenic content.
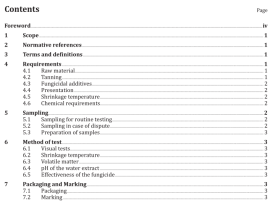
4 Reagents
During the analysis, use only reagents of recognized analytical grade and Grade 2 water in accordance with ISO 3696.
Reagents are to be selected or purified for the lowest possible blank value.
4.1 Sodium peroxide (Na 2 O 2 ).
4.2 Sodium carbonate (Na 2 CO 3 ), anhydrous powder.
4.3 Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO 3 ).
4.4 Sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
4.5 Iron oxide (Fe 2 O 3 ).
4.6 Arsenic trioxide (As 2 O 3 ).
4.7 Hydrochloric acid, ρ 1,16 g/ml to 1,19 g/ml.
4.8 Nitric acid, ρ 1,42 g/ml.
4.9 Hydrochloric acid, ρ 1,16 g/ml to 1,19 g/ml, diluted 1+1.
4.10 Hydrochloric acid, ρ 1,16 g/ml to 1,19 g/ml, diluted 2+98.
4.11 Hydrochloric acid, ρ 1,16 g/ml to 1,19 g/ml, diluted 12+88.
4.12 Sodium hydroxide solution, 40 g/l.
Dissolve 2 g of sodium hydroxide to 10 ml of water; dilute to 50 ml.
4.13 Sodium borohydride solution, 8 mg/ml.
Dissolve 0,5 g of sodium hydroxide to 10 ml of water, then dissolve 0,8 g of sodium borohydride [NaBH 4 > 95 % (m/m)] in the 50 ml beaker contained sodium hydroxide solution; dilute to 100 ml. This solution shall be freshly prepared and used immediately.
4.14 Potassium iodide solution, 100 mg/ml.
Dissolve 10 g of potassium iodide [KI > 98,5 % (m/m)] in 20 ml of water. Dilute to 100 ml.
4.15 Ascorbic acid solution, 100 mg/ml.
Dissolve 10 g of ascorbic acid [C 6 H 8 O 6 > 99,5 % (m/m)] in 20 ml of water. Dilute to 100 ml. This solution shall be freshly prepared and used immediately.