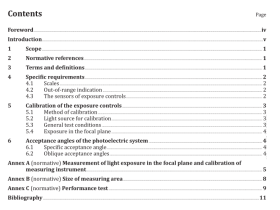
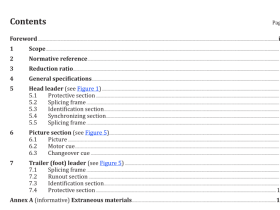
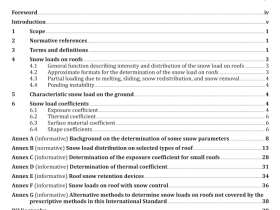
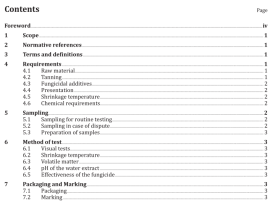
ISO 16419 pdf download
ISO 16419 pdf download Cork — Visual anomalies of cork stoppers for still wines
This International Standard applies to both
semi-elaborated natural cork stoppers and colmated natural cork stoppers at the definitivedimensions stage, and
finished natural cork stoppers and colmated natural cork stoppers ready to use.It describes theanomalies ofcorkstoppersthat can be detected byvisualexamination ofthe manufactureror the end-user.
These anomalies, according to their size, can have functional or not functional consequences being ableto alter, more or less, the cork stoppers’ sealing capacity.On the basis ofa common sampling example, this International Standard proposes for all these anomaliessome specifications for stoppers.
2 Normative references
The following documents,in whole or in part, are normatively referenced in this document and areindispensable for its application, For dated references, only the edition cited applies. For undatedreferences, the latest edition of the referenced document (including any amendments) applies.
ISO 633, Cork – Vocabulary
3 Designation for the different requirement levelsFor natural cork stoppers for still wines, the following notion of range with three decreasing levels ofrequirement is introduced:
superior range;
standard range;
entry of range.
Besides the commercial reference of the lot of cork stoppers, it belongs
to the end-user to clarify what are his/her needs in relation to these three specifications (orrange) levels,and
to the manufacturer to define to which range the lot of cork stoppers belongs.
The definite ranges do not necessarily include the total amount of usable cork stoppers for sealing; therecan also be other unanimous transactions that are out of the scope of this International Standard.
4 List ofanomalies taken into accountOnly the following will be considered cork stoppers’ anomalies:longitudinal crack;
— parasite gallery;
— green corkwood stain;
— folded corkwood;
— dry vein;
— bevel and/or bevelled cork stopper;
— back;
— colmation excess;
— machining defects (asymmetries, tool bumps, gutters);
— belly.
Other aspect irregularities are not considered as anomalies since they only affect the cork stoppers’presentation and will be taken into account in the cork stoppers’ visual classification.
In the case of having more than one anomaly with functional consequence in the same cork stopper, only the most important will be considered (penalized).
5 Anomalies of natural corkwood stoppers and colmated natural cork stoppers for still wines
Both Table 1 and Table 2 present the anomalies in relation to the raw material and to the fabrication process respectively, being:
— columns 1 and 2 – The name and definition of the anomaly in accordance with ISO 633 (Vocabulary).